This article explores the use of NVivo software for inductive coding in thematic narrative synthesis. This software was used in a review conducted by the author (Elliot-Mainwaring, 2021). The research objective of the review was to identify how power and hierarchy affect staff safety in maternity services through the methodology of a narrative synthesis of staff voices from relevant literature. The aim was to discuss staff safety in effectively speaking out, while acknowledging that patients are receiving poor care. The author's question was that if patients are saying that they are receiving poor care, what are the staff saying? Power and hierarchy may have positive influences on staff safety; however, the search strategy employed within the study ensured a particular focus on the adverse impact for the synthesis. Justification for this topic of enquiry has already been discussed in the previous paper ‘How do power and hierarchy influence staff safety in maternity services?’ (Elliott-Mainwaring, 2021). This article focuses on an evaluation of using NVivo as a novice user within a narrative synthesis.
Narrative approaches to create systematic reviews of lived experiences focus on textual evidence, likely recordings from interviews transcribed with consent, or even diary content (Pope et al, 2006). Dixon-Woods et al (2005) have previously expressed concern at the lack of transparency in the process of creating a narrative synthesis, and so NVivo software fills this niche by providing a clear pathway of evidence in the researcher's decision making on their journey to processing narrations. For a credible narrative synthesis to work, the voices from likeminded research papers are combined or synthesised to create fresh understandings in a more nuanced way. However, Martin et al (2021) are clear that the process of encouraging employee voice must also recognise much wider institutional sociocultural issues influencing staff decision making, it could never be just about creating opportunities to speak. Findings from narrative synthesis systematic reviews have the potential to influence future policies in healthcare or employment practices (Snilstveit et al, 2012).
NVivo works as a software package with the capacity to store data in a centralised area. There are options for in depth analysis of uploaded data, such as preloading research frameworks, or as in the case of this study, allowing the data to speak for itself in an iterative manner with the emergence of codes during the research process. Patterns and themes evolve as the package is used and there are many visualisation options for cross referencing and pulling out data in terms of graphs, word art and frequency plots. There are collaboration possibilities with this software, so that larger projects can be shared and educational supervisors can have oversight of students work (QSR International, 2021).
Use of NVivo to apply iterative reflexivity was embedded in the methodology of the research as a transparent strategy (Patnaik, 2013; Berger, 2015), with the same sequence of analysis applied to each paper through NVivo software, exploring relationships and reflecting on this research process throughout (Edwards and Kaimel, 2016). This was not by design a linear process of research, but rather the development of new understanding as the narrative synthesis unfolded (Seers, 2012; Snilstveit et al, 2012; Edwards and Kaimel, 2016). The purpose of this paper is to discuss the method with the application of NVivo software.
Methods
This study was based on the approach of a ‘textual narrative synthesis of the literature relevant to the subject matter’ (Barnett-Page and Thomas, 2009). A literature search was conducted of a number of databases and selected papers were coded inductively using NVivo software, which could be seen as a subjective idealist approach to knowledge where iteration is achieved at the coding and synthesis stages of the process. Full details of the review, its methods and its results have already been published (Elliot-Mainwaring, 2021).
The license for using NVivo was provided by the author's place of study, The University of Leicester. The process of coding each research paper was initially challenging. The author used YouTube videos and NVivo support to guide them through setting up a project and importing the individual pdfs (Rich and Patashnick, 2002; Welsh, 2002; QSR International, 2021). NVivo proved to be versatile in that the imported files could be word or pdf. The Import tab made it possible to upload images and audio files. Information could be transferred from OneNote, Outlook and bibliographic software such as Endnote and RefWorks.
Initially, the uploaded selected papers stored in Data Files were read by the author, to get a feel for their content, and then by accessing the Create tab, the author highlighted sentences and coded them into nodes, which were created as the process progressed. NVivo coding works creates parent and child nodes, which are units of data selected by the user and for which relationships can then be dependently allocated. This has the potential to create an interwoven story. These codes and nodes were amalgamated as different themes arose and ideas were then synthesised across the papers. This iterative design meant that the analysis grew in a non-linear manner (rather than having a pre-set deductive framework from which to box off data as highlighted, which is another way of coding). The author moved child nodes and changed relationships between ideas as the narratives of the participants were analysed.
Results
The NVivo software options in the Explore tab for reviewing data illustrated that the coding was robust. Figure 1 shows the coding process for psychological vulnerability as an exploration of the coding relationships between the papers. This is shown to illustrate the links made between papers, leaving none uncoded in this synthesis of 10 shortlisted papers. More software options included the option to review the papers clustered by coding similarity (Figure 2) and to review papers by Word Clouds (Figure 3). Histograms, hierarchies and cluster analysis are also available. Table 1 tabulates the final coded narrative analysis.
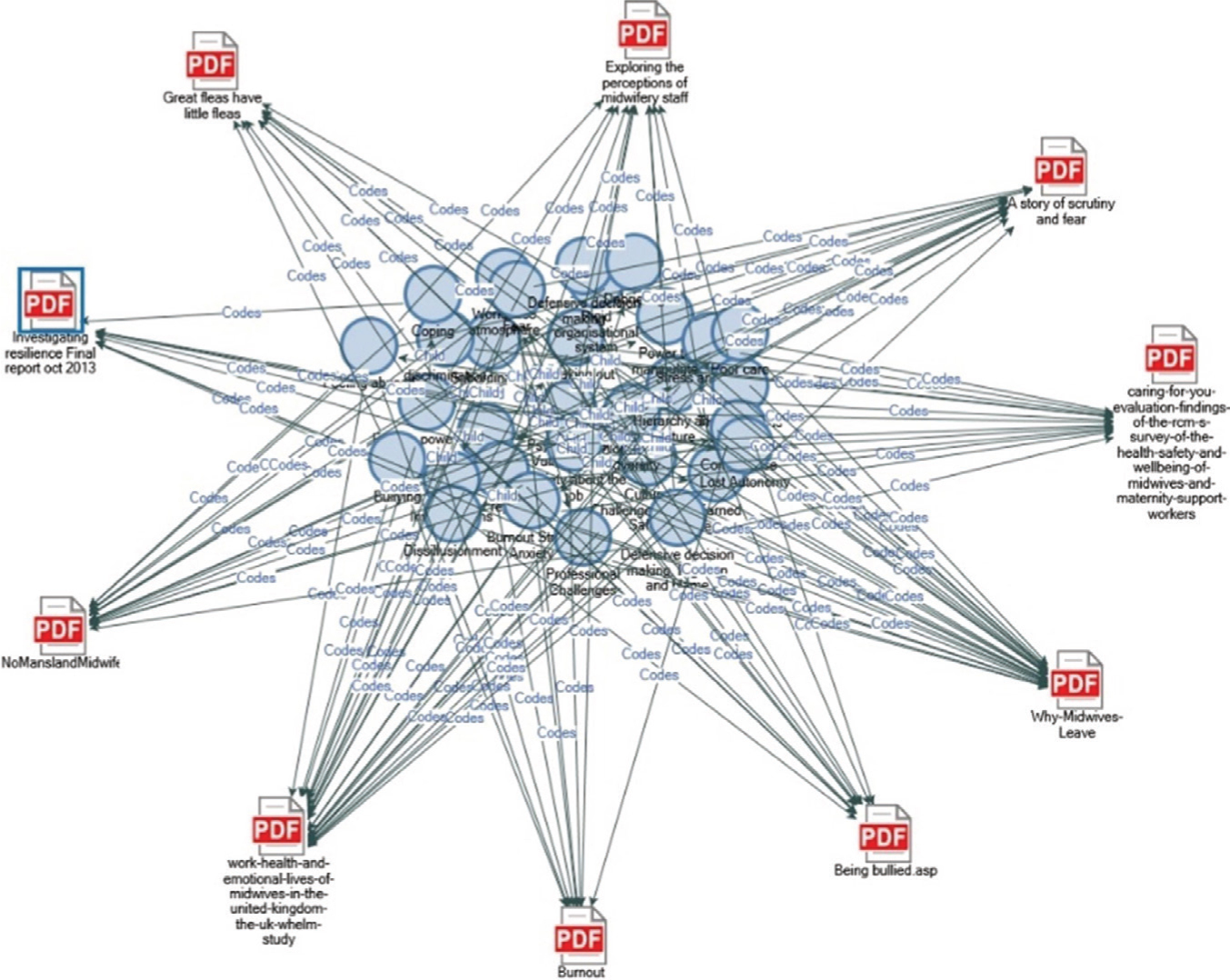 Figure 1. Psychological vulnerability exploration of coding relationships between papers explored
Figure 1. Psychological vulnerability exploration of coding relationships between papers explored  Figure 2. Narrative synthesis tree of papers coded
Figure 2. Narrative synthesis tree of papers coded  Figure 3. Word clouds with stemmed words
Figure 3. Word clouds with stemmed words
Table 1. NVivo coded narrative analysis
| Research question | Scope | Analytical themes | Descriptive themes | Themes | Subthemes | Files | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subordination | 7 | 19 | |||||
| Speaking out | 8 | 38 | |||||
| Feeling powerless | 10 | 84 | |||||
| Bullying | 10 | 78 | |||||
| Burnout/stress/anxiety | 5 | 58 | |||||
| Fear of investigation | 9 | 64 | |||||
| Rigid organisation system | 6 | 34 | |||||
| Poor care | 4 | 22 | |||||
| Compromise to survive | 3 | 9 | |||||
| Psychological vulnerability | Anxiety about job and relationships | Cultural normalisation | Workplace atmosphere | 6 | 44 | ||
| Challenges to staff safety | Workplace adversity | Dysfunctional relationships | |||||
| Working conditions | Poor organisation and structural conditions | Institutional normalisation | Poor communication | 6 | 36 | ||
| Staff engagement | 6 | 13 | |||||
| Personal challenges | 6 | 10 | |||||
| Quality of care | 7 | 21 | |||||
| Exhaustion | 5 | 21 | |||||
| Dangerous workloads | 7 | 58 | |||||
| Pay | 3 | 16 | |||||
| Inflexibility | 7 | 15 | |||||
| Low morale | 8 | 26 | |||||
| Lack of breaks | 6 | 30 | |||||
| Challenges to resilience | 7 | 61 |
The disadvantages of using NVivo were that it was a time-consuming piece of software to learn how to use, although the many YouTube videos that are available do offer support for both Mac and Word users. The university NVivo contract was due for renewal over the summer of 2020, and this meant that without warning the data were frozen. Frequent logins to NVivo will alert users to renewals of key codes provided by licence shown on a countdown with days and options on how often users would like to be reminded, but this is only useful if regularly accessing the NVivo software. Having completed the coding, the author discovered that this was an issue when they retrospectively entered their account to clarify a finding several weeks later. Users of this software may wish to be aware that this is perhaps a specific university issue, and not necessarily a fault with the product.
Discussion
Figure 2 displays the coding relationships of the 10 chosen papers, presented in a tree diagram using NVivo software. Begley (2002) and Hunter and Warren (2013) both shared a branch as these papers described resilience tactics. The remaining papers were naturally separated into three research papers exploring the lives of midwives past and present (Hunter and Henley, 2019; Royal College of Midwive, 2016; 2017). Currie and Richens (2009) alongside Hood et al (2010) shared similar safety themes; and Capper et al (2020), Young et al (2015) and Davies and Coldridge (2015) explored the repercussions for staff.
This synthesis achieved heterogeneity in that the participants involved came from different locations around the globe, and papers incorporated feedback from support workers, students and midwives. Qualitative evidence synthesis as a research methodology was introduced by Noblit and Hare (1988), in which the findings of qualitative research are reviewed and synthesised into meaningful data (Noblit and Hare, 1988; Thorne et al, 2004; Houghton et al, 2016). A narrative synthesis approach was selected as this has the advantage of researching in a storied manner, rather than fragmenting the involved staff narratives, which the author felt would be the result with thematic analysis. Others who have researched staff experience of healthcare with this method include Bloomer and Walshe (2020), Wyder et al (2017) and Connolly et al (2021). Dixon-Woods et al (2006) warned against the imposition of dominant methods for reviewing qualitative research in order to foster innovation, cautioning reflexivity with whichever technique is applied to allow other researchers to benefit from their synthesis experiences.
Conclusions
NVivo was a user-friendly tool for a novice user, facilitating coding for thematic narrative synthesis. Discovered themes are shown in Table 1 and discussion of these findings are explored in a further paper (Elliott-Mainwaring, 2021).
The process of inductive coding took several weeks to achieve and undoubtably a different team approaching this research topic would have altered the methodology by potentially changing the selection of papers to synthesise, and perhaps achieved a different conclusion. However, the use of NVivo software was impressive and suggests that possibilities are available to explore this package further at Doctorate level.
Key points
- Qualitative evidence synthesis is a research methodology in which the findings of qualitative research are reviewed and synthesised into meaningful data
- Dixon-Woods et al warned against the imposition of dominant methods for reviewing qualitative research in order to foster innovation, cautioning reflexivity with whichever technique is applied to allow other researchers to benefit from their synthesis experiences
- Iterative reflexivity was embedded into the methodology of this research as a strategy with the same sequence of analysis applied to each paper through NVivo software, exploring relationships and reflecting on this research process throughout
- This was not by design a linear process of research, but rather new understanding developed as the narrative synthesis unfolded through using software coding
CPD reflective questions
- How can you as a practising midwife ensure that any information or advice given is evidence based?
- To what extent do you feel able to take account of current evidence, knowledge and developments in reducing mistakes?
- What enables you to work with colleagues and realise the impact of human factors on system failures?
- Do you feel able to deal with differences of professional opinion?
- What can be done to support healthcare staff in quality improvement initiatives?


